Opto-twistronic Hall effect in a three-dimensional spiral lattice | Nature
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07949-1
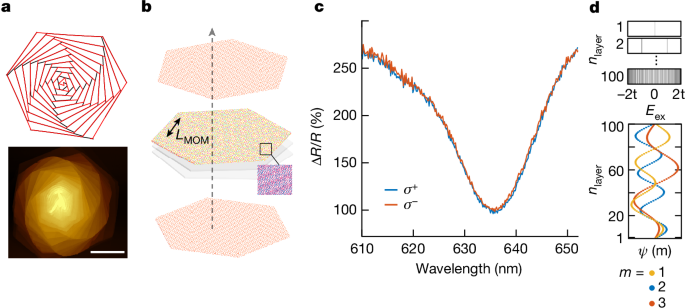
Studies of moiré systems have explained the effect of superlattice modulations on their properties, demonstrating new correlated phases1. However, most experimental studies have focused on a few layers in two-dimensional systems. Extending twistronics to three dimensions, in which the twist extends into the third dimension, remains underexplored because of the challenges associated with the manual stacking of layers. Here we study three-dimensional twistronics using a self-assembled twisted spiral superlattice of multilayered WS2. Our findings show an opto-twistronic Hall effect driven by structural chirality and coherence length, modulated by the moiré potential of the spiral superlattice. This is an experimental manifestation of the noncommutative geometry of the system. We observe enhanced light–matter interactions and an altered dependence of the Hall coefficient on photon momentum. Our model suggests contributions from higher-order quantum geometric quantities to this observation, providing opportunities for designing quantum-materials-based optoelectronic lattices with large nonlinearities. Opto-twistronic Hall effect driven by structural chirality and coherence length is observed in a three-dimensional self-assembled twisted spiral superlattice of WS2.