The U.S. Military Can’t Solve the Fentanyl Crisis
The U.S. Military Can’t Solve the Fentanyl Crisis
https://foreignpolicy.com/2023/09/08/us-military-fentanyl-mexico-colombia-cocaine-cartel/
A trendy idea among GOP candidates would fail, just as it did in Colombia.

Reducing the harms of xylazine: clinical approaches, research deficits, and public health context - Harm Reduction Journal [2023]
Reducing the harms of xylazine: clinical approaches, research deficits, and public health context - Harm Reduction Journal
https://harmreductionjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12954-023-00879-7
Objectives Xylazine has emerged as a consistent part of the unregulated drug supply in recent months. We discuss major domains of xylazine’s harm, current knowledge deficits, clinical and harm reduction strategies for minimizing harm, and xylazine’s public health and policy context. As an interdisciplinary team from across the USA, we have pooled our knowledge to provide an overview of xylazine’s current and emerging contexts. Methods To inform this essay, the pertinent literature was reviewed, clinical knowledge and protocols were shared by multiple clinicians with direct expertise, and policy and public health context were added by expert authors. Results We describe xylazine’s major harm domains—acute poisoning, extended sedation, and wounds, along with anemia and hyperglycemia, which have been reported anecdotally but lack as clear of a connection to xylazine. Current successful practices for xylazine wound care are detailed. Understanding xylazine’s epidemiology will also require greater investment in drug checking and surveillance. Finally, approaches to community-based wound care are discussed, along with an orientation to the larger policy and public health context. Conclusions Addressing the harms of xylazine requires interdisciplinary participation, investment in community-based harm reduction strategies, and improved drug supply surveillance. The relatively unique context of xylazine demands buy-in from public health professionals, harm reduction professionals, clinicians, basic science researchers, policymakers and more.

Psilocybin analog 4-OH-DiPT enhances fear extinction and GABAergic inhibition of principal neurons in the basolateral amygdala - Neuropsychopharmacology [2023]
Psilocybin analog 4-OH-DiPT enhances fear extinction and GABAergic inhibition of principal neurons in the basolateral amygdala - Neuropsychopharmacology
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41386-023-01744-8
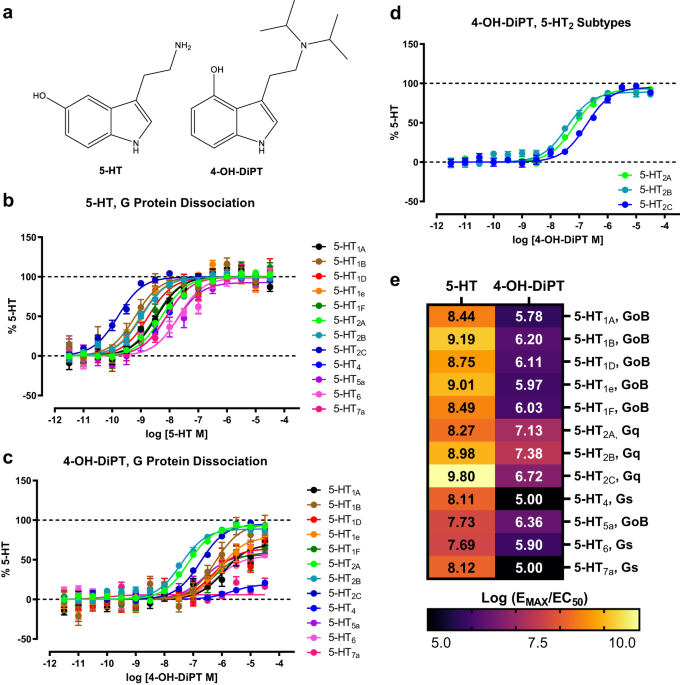
Psychedelics such as psilocybin show great promise for the treatment of depression and PTSD, but their long duration of action poses practical limitations for patient access. 4-OH-DiPT is a fast-acting and shorter-lasting derivative of psilocybin. Here we characterized the pharmacological profile of 4-OH-DiPT and examined its impact on fear extinction learning as well as a potential mechanism of action. First, we profiled 4-OH-DiPT at all 12 human 5-HT GPCRs. 4-OH-DiPT showed strongest agonist activity at all three 5-HT2A/2B/2C receptors with near full agonist activity at 5-HT2A. Notably, 4-OH-DiPT had comparable activity at mouse and human 5-HT2A/2B/2C receptors. In a fear extinction paradigm, 4-OH-DiPT significantly reduced freezing responses to conditioned cues in a dose-dependent manner with a greater potency in female mice than male mice. Female mice that received 4-OH-DiPT before extinction training had reduced avoidance behaviors several days later in the light dark box, elevated plus maze and novelty-suppressed feeding test compared to controls, while male mice did not show significant differences. 4-OH-DiPT produced robust increases in spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) in basolateral amygdala (BLA) principal neurons and action potential firing in BLA interneurons in a 5-HT2A-dependent manner. RNAscope demonstrates that Htr2a mRNA is expressed predominantly in BLA GABA interneurons, Htr2c mRNA is expressed in both GABA interneurons and principal neurons, while Htr2b mRNA is absent in the BLA. Our findings suggest that 4-OH-DiPT activates BLA interneurons via the 5-HT2A receptor to enhance GABAergic inhibition of BLA principal neurons, which provides a potential mechanism for suppressing learned fear.